Would you believe me if I told you that Evergreen and the City of San Jose had a Mayor Quimby over 125 years before the Simpsons? Matt Groening’s portrait of the Mayor couldn’t contrast our factual character more. I’m going to try to provide you with an accurate portrait of our fair-minded Mayor, John Alonzo Quimby. I was lucky enough to find a contemporary family source in a Genealogical History for the Quimby Family from 1915, though newspapers and political publications didn’t say much..
Would you believe me if I told you that Evergreen and the City of San Jose had a Mayor Quimby over 125 years before the Simpsons? Matt Groening’s portrait of the Mayor couldn’t contrast our factual character more. I’m going to try to provide you with an accurate portrait of our fair-minded Mayor, John Alonzo Quimby. I was lucky enough to find a contemporary family source in a Genealogical History for the Quimby Family from 1915, though newspapers and political publications didn’t say much..
 Quimby as a name is fairly popular in England, where its origins are traced back to the 11th century. Though probably Germanic in origin and possibly Hebrew in its roots, the Quimby name, its variations (Quinby, Quinbee, Quenby, possibly Quincy, etc.) and its coat of arms are found all over England. It dates back to an ancient Welsh King, The Quimby Family came from a long line of Colonialists and Quakers. The ancient family would come to Salem, then Massachussetts colony as early as 1640, seeking freedom from the religious persecution that brought so many people to America at the time. They were not rumored in Salem Witch Hunts, but one relative died in heated fights with the Native Americans there. His ancestors would’ve fought to create this country.
Quimby as a name is fairly popular in England, where its origins are traced back to the 11th century. Though probably Germanic in origin and possibly Hebrew in its roots, the Quimby name, its variations (Quinby, Quinbee, Quenby, possibly Quincy, etc.) and its coat of arms are found all over England. It dates back to an ancient Welsh King, The Quimby Family came from a long line of Colonialists and Quakers. The ancient family would come to Salem, then Massachussetts colony as early as 1640, seeking freedom from the religious persecution that brought so many people to America at the time. They were not rumored in Salem Witch Hunts, but one relative died in heated fights with the Native Americans there. His ancestors would’ve fought to create this country.
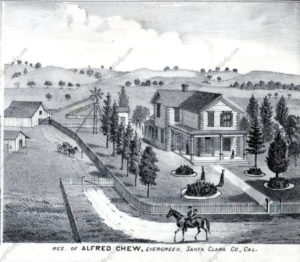
 John A. Quimby would be born in Parsippany, New Jersey in 1818 to affluent, well respected parents. His father would be a politician in New England. Quimby’s father originally ran the lucrative family shoe making business before running for judge and serving the County court system 25-30 years in New Jersey. His brother, Isaac, would be a General for the Union Army during the Civil War. This is his famous brother from Back East to the right who eventually became a US Marshall. My historian’s note here would be that photographs through the 1800’s would only be taken by the rich and famous or very large groups. It was an infant of an art and a science as well as expensive to do. Strangely enough, the politically minded family were Democrats for the most part, with the exception of our Mayor. This may be the reason the Republican pioneer came to California in 1846. Regardless, this photograph from the mid 1800’s should prove how well respected John Alonzo Quimby was.
John A. Quimby would be born in Parsippany, New Jersey in 1818 to affluent, well respected parents. His father would be a politician in New England. Quimby’s father originally ran the lucrative family shoe making business before running for judge and serving the County court system 25-30 years in New Jersey. His brother, Isaac, would be a General for the Union Army during the Civil War. This is his famous brother from Back East to the right who eventually became a US Marshall. My historian’s note here would be that photographs through the 1800’s would only be taken by the rich and famous or very large groups. It was an infant of an art and a science as well as expensive to do. Strangely enough, the politically minded family were Democrats for the most part, with the exception of our Mayor. This may be the reason the Republican pioneer came to California in 1846. Regardless, this photograph from the mid 1800’s should prove how well respected John Alonzo Quimby was.
Mayor Quimby first studied law and practiced with a Judge in New Jersey. John Alonzo Quimby would come to California as early as 1846 with his father, but definitely arrived in Santa Clara County by 1849 with his first wife, Minerva Moody of New York. It was said before leaving New Jersey that J. A. Quimby was one of Morristown, New Jersey’s best orators and they had a few.
 John Alonzo Quimby would become entangled with California’s State Affairs early on, even running for US Senator at one point. Quimby was present, along with delegate Charles White, at the “Legislature of A Thousand Drinks”, held in San Jose in 1849. This Assembly would create California’s State Constitution and the creation of its Capitol, in San Jose. In 1850, Quimby would see the need and build the first roadway from Santa Cruz to San Jose, laying the groundwork for Highway 17 today. John would engage in the lumber business there as a City developed in the Valley. The Captiol would move to Vallejo in 1851, and to Sacramento. Even still, the site of the Capitol would become a second epicenter for the City of San Jose. Quimby would be in the California legislature from 1855 to 1858 and be San Jose’s Mayor for two terms from 1863-1869. J. A. Quimby would later be on the Board of County Supervisors for two terms.
John Alonzo Quimby would become entangled with California’s State Affairs early on, even running for US Senator at one point. Quimby was present, along with delegate Charles White, at the “Legislature of A Thousand Drinks”, held in San Jose in 1849. This Assembly would create California’s State Constitution and the creation of its Capitol, in San Jose. In 1850, Quimby would see the need and build the first roadway from Santa Cruz to San Jose, laying the groundwork for Highway 17 today. John would engage in the lumber business there as a City developed in the Valley. The Captiol would move to Vallejo in 1851, and to Sacramento. Even still, the site of the Capitol would become a second epicenter for the City of San Jose. Quimby would be in the California legislature from 1855 to 1858 and be San Jose’s Mayor for two terms from 1863-1869. J. A. Quimby would later be on the Board of County Supervisors for two terms.

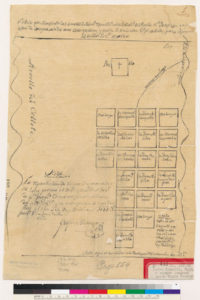
 The well-respected lawmaker would become the creator of the Downtown San Jose we know nowadays. For the sake of contract, the map to the right is San Jose in 1847. It has a single road, the El Camino Real, today’s Alameda turning into Santa Clara beyond this point. It’s layout is logical, like the numbered street we know, and it has well known San Jose founders sprinkled in. The Guadalupe River creates a border for the small city. At this point a lot of today’s Downtown isn’t even a thought. In 1847, an acre of land downtown like these would cost $50.00. Through his initiatives, crucial issues that arose in San Jose at California’s birth were solved through Mayor Quimby’s terms in office.
The well-respected lawmaker would become the creator of the Downtown San Jose we know nowadays. For the sake of contract, the map to the right is San Jose in 1847. It has a single road, the El Camino Real, today’s Alameda turning into Santa Clara beyond this point. It’s layout is logical, like the numbered street we know, and it has well known San Jose founders sprinkled in. The Guadalupe River creates a border for the small city. At this point a lot of today’s Downtown isn’t even a thought. In 1847, an acre of land downtown like these would cost $50.00. Through his initiatives, crucial issues that arose in San Jose at California’s birth were solved through Mayor Quimby’s terms in office.
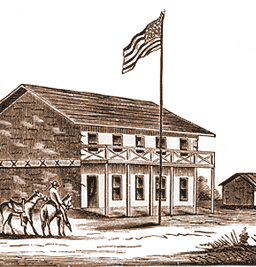 The Market Square was always a meeting place for the Pueblo of San Jose and so it only seemed fitting to hold California’s first meeting in California’s first civic meeting place. In 1797, the Spanish would raise a Town Hall at the site for parades and City meetings. There would be reports of ill maintained hotels and flooding at Market Square, which encouraged the Capitol’s relocation to Vallejo. A dam would need to be built for the Guadalupe River to keep the Capitol dry. This building still used in 1851 for San Jose’s administration, John A. Quimby would inherit San Jose with its run down buildings and infrastructure. The Fire Department had no firehouse and broken down engines. City Hall’s walls were crumbing. After all, it was over 65 years old by the time he got to City Hall. Furthermore, in 1863, the disputes created by settlement were still creating tensions.
The Market Square was always a meeting place for the Pueblo of San Jose and so it only seemed fitting to hold California’s first meeting in California’s first civic meeting place. In 1797, the Spanish would raise a Town Hall at the site for parades and City meetings. There would be reports of ill maintained hotels and flooding at Market Square, which encouraged the Capitol’s relocation to Vallejo. A dam would need to be built for the Guadalupe River to keep the Capitol dry. This building still used in 1851 for San Jose’s administration, John A. Quimby would inherit San Jose with its run down buildings and infrastructure. The Fire Department had no firehouse and broken down engines. City Hall’s walls were crumbing. After all, it was over 65 years old by the time he got to City Hall. Furthermore, in 1863, the disputes created by settlement were still creating tensions.
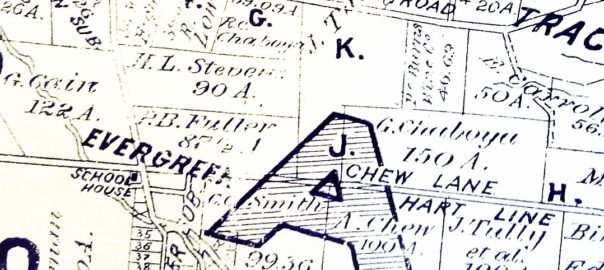
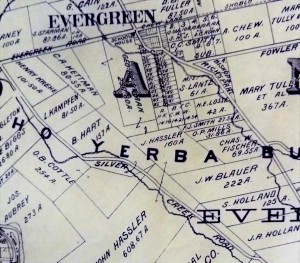
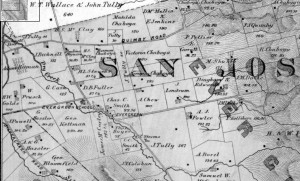
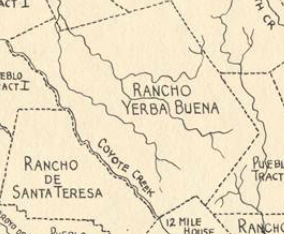
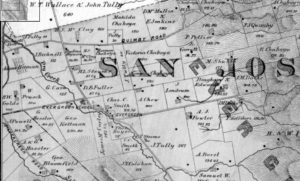
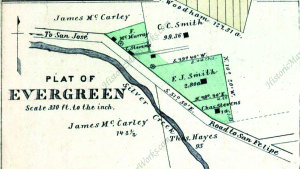
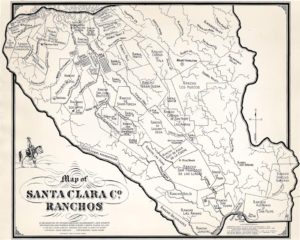
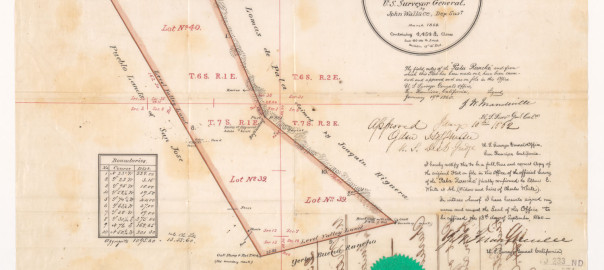
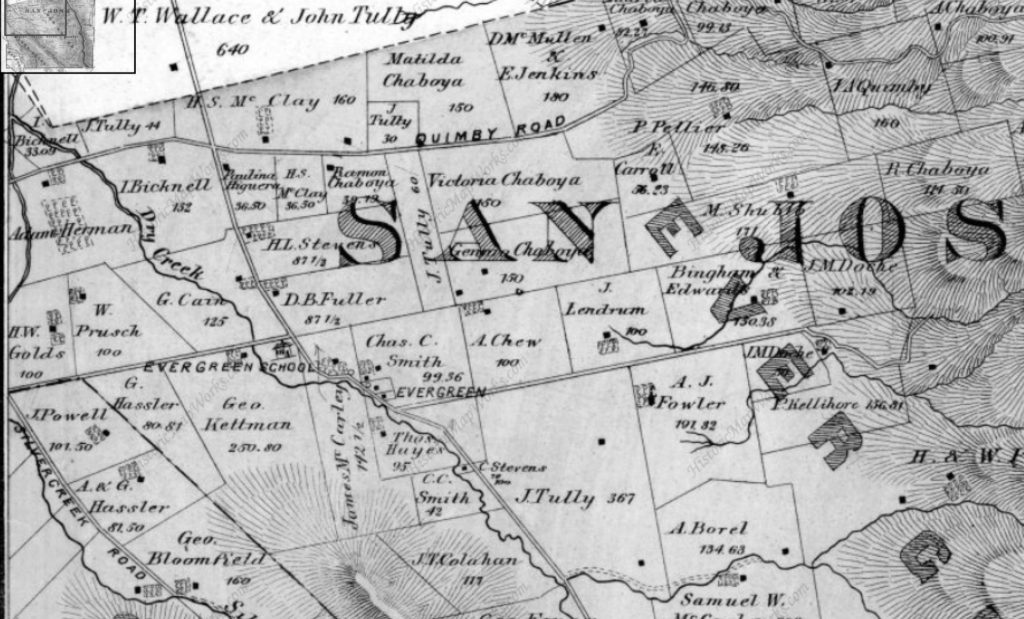 Rancho Yerba Buena wasn’t up for dispute anymore. John Alonzo Quimby himself legally purchased a large ranch 3 miles from Downtown Evergreen, next door to the Pellier Family, near where the Middle School stands today but up the road a little ways. Victoria Chaboya’s property is more likely where the Quimby Oak Middle School stands today. Oak trees are a main feature of Evergreen, not pine trees. Quimby Oak rather rathers to the bed of Oak trees gathering along the Quimby Creek, running though Quimby and Pellier’s properties. Quimby Road would always run past his Evergreen hills property. J. A. Quimby was able to purchase a Creekside property near where the Chaboyas themselves called home. The California Government didn’t uphold all of the Mexican land grants like the Chaboyas. In fact, Rancho Yerba Buena was the exception to the rule in Santa Clara County.
Rancho Yerba Buena wasn’t up for dispute anymore. John Alonzo Quimby himself legally purchased a large ranch 3 miles from Downtown Evergreen, next door to the Pellier Family, near where the Middle School stands today but up the road a little ways. Victoria Chaboya’s property is more likely where the Quimby Oak Middle School stands today. Oak trees are a main feature of Evergreen, not pine trees. Quimby Oak rather rathers to the bed of Oak trees gathering along the Quimby Creek, running though Quimby and Pellier’s properties. Quimby Road would always run past his Evergreen hills property. J. A. Quimby was able to purchase a Creekside property near where the Chaboyas themselves called home. The California Government didn’t uphold all of the Mexican land grants like the Chaboyas. In fact, Rancho Yerba Buena was the exception to the rule in Santa Clara County.
 Many were stripped of their holdings and left tiny portions of their former farms, including Antonio Chaboya’s brothers, by US Surveyors. The railroad into San Jose was completed in 1863, when Quimby first became Mayor. The land grab created room for new immigrants and U.S. citizens in early San Jose, which there were plenty arriving and on their way. The first secular development in California, established in 1777, had been growing from the epicenter of Mission de Santa Clara de Asis, today’s Santa Clara University. These homes, though close, were large and had adequate yards. If these people were also farmers, though, their farms or vacation homes would be elsewhere, in modern day suburban communities surrounding San Jose’s Downtown. To the right is Downtown San Jose looking towards the Mission in 1866, when J. A. Quimby was Mayor.
Many were stripped of their holdings and left tiny portions of their former farms, including Antonio Chaboya’s brothers, by US Surveyors. The railroad into San Jose was completed in 1863, when Quimby first became Mayor. The land grab created room for new immigrants and U.S. citizens in early San Jose, which there were plenty arriving and on their way. The first secular development in California, established in 1777, had been growing from the epicenter of Mission de Santa Clara de Asis, today’s Santa Clara University. These homes, though close, were large and had adequate yards. If these people were also farmers, though, their farms or vacation homes would be elsewhere, in modern day suburban communities surrounding San Jose’s Downtown. To the right is Downtown San Jose looking towards the Mission in 1866, when J. A. Quimby was Mayor.
 Mission Santa Clara feels like the outskirts of Downtown today. You’re totally right. What we feel like is Downtown today, First and Santa Clara Streets, would be John Alonzo Quimby’s impact on San Jose. The one time Capitol, brought by delegates White and Reed and witnessed by Quimby no doubt, would be today’s Cesar Chavez Square on Market Street. This would become a second burst of growth in San Jose’s adolescence. Downtown is something different because of this second epicenter. The bustling City would then center around Market and Santa Clara Streets, adding to the numbered streets and narrowing their lots.
Mission Santa Clara feels like the outskirts of Downtown today. You’re totally right. What we feel like is Downtown today, First and Santa Clara Streets, would be John Alonzo Quimby’s impact on San Jose. The one time Capitol, brought by delegates White and Reed and witnessed by Quimby no doubt, would be today’s Cesar Chavez Square on Market Street. This would become a second burst of growth in San Jose’s adolescence. Downtown is something different because of this second epicenter. The bustling City would then center around Market and Santa Clara Streets, adding to the numbered streets and narrowing their lots.
 Then, during his Mayoral office, Quimby would bring together both parties to handle the disputes, fill San Jose’s Treasury by selling small “pueblo” lots Downtown and create services for the growing population. Contemporaries would explain that the Cities of San Jose and Santa Clara were already touching and growing denser down the Alameda. Plots were being sold for $50.00 an acre or city block around the Alameda and St. James Park. Once Quimby took office, an acre cost $200.00. US Surveyors would bring into question some of the $50.00 acres, allowing farms downtown to be broken up into subdivisions. $50.00 plots were still being developed, however. The City of San Jose would be considered as far east as Coyote Creek, as far south as Bird Avenue, as far west as Meridian Avenue and as far north as Hedding Street. Quimby would improve the roadway system and rejuvenate San Jose’s infrastructure with the raising of funds, replacing rundown equipment and buildings. Many of San Jose’s oldest standing buildings come from the Quimby era. With a focus shifted away from the Mission and towards developing outward from the City Plaza, Cesar Chavez Park, Downtown San Jose’s small lots still exist today. The numbered streets are a result of many of Quimby’s decisions. He killed two very big birds with one very awesome stone that still can be felt today. To the left is a map of San Jose shortly after he left City Hall.
Then, during his Mayoral office, Quimby would bring together both parties to handle the disputes, fill San Jose’s Treasury by selling small “pueblo” lots Downtown and create services for the growing population. Contemporaries would explain that the Cities of San Jose and Santa Clara were already touching and growing denser down the Alameda. Plots were being sold for $50.00 an acre or city block around the Alameda and St. James Park. Once Quimby took office, an acre cost $200.00. US Surveyors would bring into question some of the $50.00 acres, allowing farms downtown to be broken up into subdivisions. $50.00 plots were still being developed, however. The City of San Jose would be considered as far east as Coyote Creek, as far south as Bird Avenue, as far west as Meridian Avenue and as far north as Hedding Street. Quimby would improve the roadway system and rejuvenate San Jose’s infrastructure with the raising of funds, replacing rundown equipment and buildings. Many of San Jose’s oldest standing buildings come from the Quimby era. With a focus shifted away from the Mission and towards developing outward from the City Plaza, Cesar Chavez Park, Downtown San Jose’s small lots still exist today. The numbered streets are a result of many of Quimby’s decisions. He killed two very big birds with one very awesome stone that still can be felt today. To the left is a map of San Jose shortly after he left City Hall.
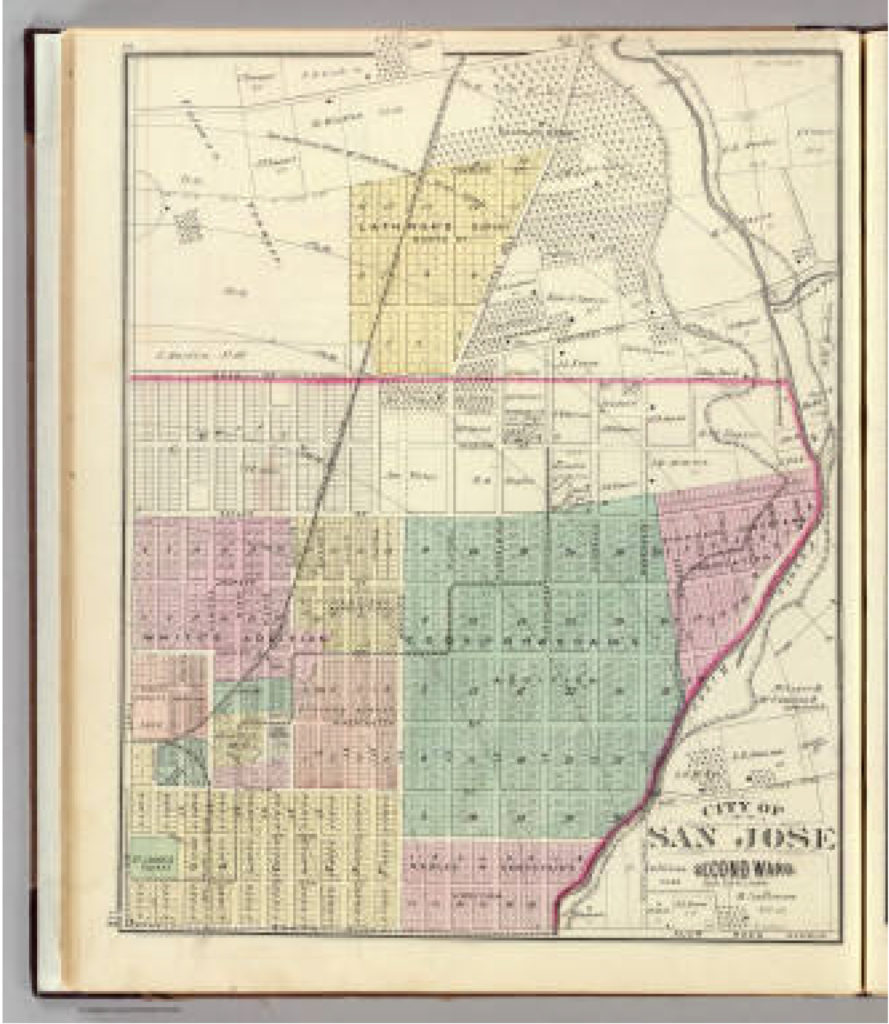
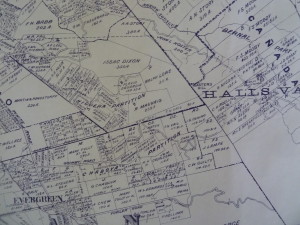
 This is a map of San Jose while John Alonzo Quimby was on the Board of County Supervisors. The rapid growth was prolific. In 4 years, San Jose would need to be broken up into huge portions. This is our modern downtown. The First Ward is the old downtown. Also notice that our Norths between the previous 2 maps are different. That was just to make this one look pretty. It’s ok. Our 1847 Map had Guadalupe through then San Jose’s west on the bottom of the map. Only a couple of those original rectangle bought for $50.00 still existed. Most were these tiny boxes in 1876. The colored portiosn are additions onto San Jose made during Quimby’s term.
This is a map of San Jose while John Alonzo Quimby was on the Board of County Supervisors. The rapid growth was prolific. In 4 years, San Jose would need to be broken up into huge portions. This is our modern downtown. The First Ward is the old downtown. Also notice that our Norths between the previous 2 maps are different. That was just to make this one look pretty. It’s ok. Our 1847 Map had Guadalupe through then San Jose’s west on the bottom of the map. Only a couple of those original rectangle bought for $50.00 still existed. Most were these tiny boxes in 1876. The colored portiosn are additions onto San Jose made during Quimby’s term.

 In 1860, San Jose would have 1000 residents. By 1868, that had been multiplied to 7000 residents. Having great leadership at the helm of a storm like that allows the transition to go smoothly. John A. Quimby found a way to make room, make jobs, and revive an aging city. He was also there at igniting of the Santa Clara County’s Fruit Industry. Quimby would create the foundation for the large city with a dense downtown we enjoy today. The San Jose Water Company was incorporated in 1866. Gas services was introduced to San Jose in 1861, but the need for expanding those pipe systems were crucial. The Normal School, today’s San Jose State University, would become State run in 1862. The courthouse was built in 1867, now the St. James Post Office though its down was burned down some time ago. The first public transit systems were in place in 1868, running down First Street to the domed courthouse. The lightrail stops there today. Does that make is a nearly 150 year old tradition to ride the modern trolley through Downtown? The Canning Industry would be underway in San Jose in 1871. Though Quimby gets the bulk of credit for the way he settled Downtown land disputes, he’s often overlooked during this crucial time in San Jose’s development. Why he’s overlooked in unknown, because he seems to be well-respected by his contemporaries and loved ones.
In 1860, San Jose would have 1000 residents. By 1868, that had been multiplied to 7000 residents. Having great leadership at the helm of a storm like that allows the transition to go smoothly. John A. Quimby found a way to make room, make jobs, and revive an aging city. He was also there at igniting of the Santa Clara County’s Fruit Industry. Quimby would create the foundation for the large city with a dense downtown we enjoy today. The San Jose Water Company was incorporated in 1866. Gas services was introduced to San Jose in 1861, but the need for expanding those pipe systems were crucial. The Normal School, today’s San Jose State University, would become State run in 1862. The courthouse was built in 1867, now the St. James Post Office though its down was burned down some time ago. The first public transit systems were in place in 1868, running down First Street to the domed courthouse. The lightrail stops there today. Does that make is a nearly 150 year old tradition to ride the modern trolley through Downtown? The Canning Industry would be underway in San Jose in 1871. Though Quimby gets the bulk of credit for the way he settled Downtown land disputes, he’s often overlooked during this crucial time in San Jose’s development. Why he’s overlooked in unknown, because he seems to be well-respected by his contemporaries and loved ones.
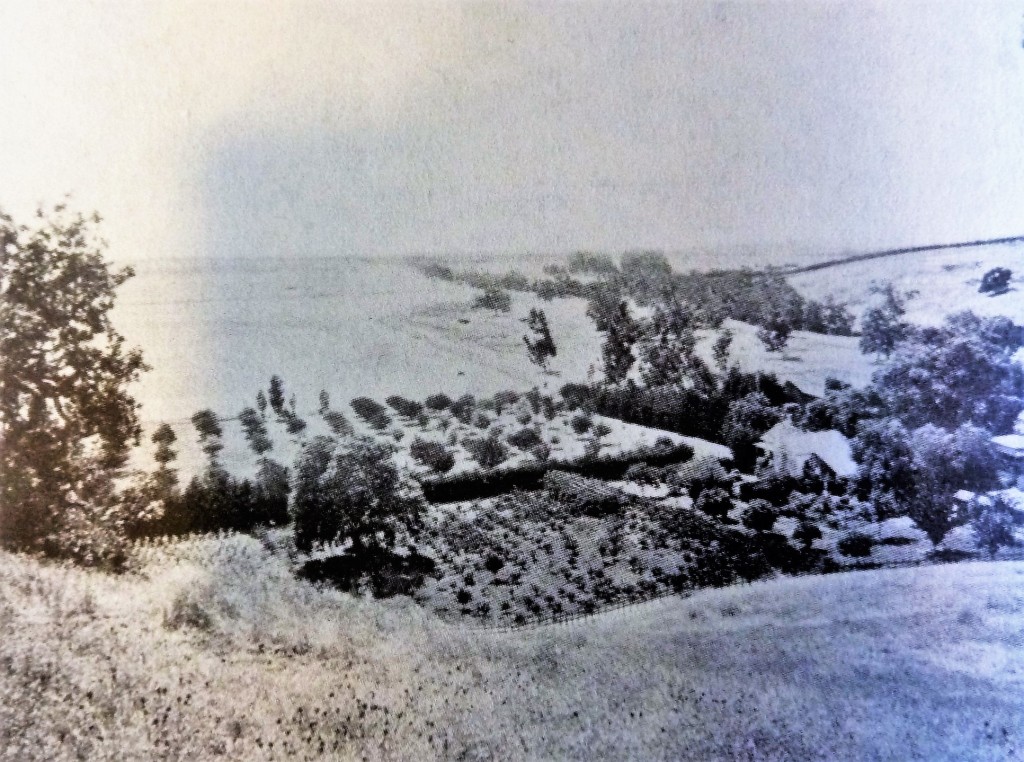
 John and Minerva would have four kids, while maintaining his political life. Minerva Moody would pass away in 1866, while he was Mayor, and John Alonzo Quimby would remarry the following year. Irene Kamp, the new Mrs. Quimby, and John would have another two children who were also raised in Evergreen. After serving the County for a number of years, John Quimby would become sick for a number of years starting in 1886. Following the illness, Quimby retired from public life to his Evergreen farm. It was said that he too raised vineyards in the Evergreen hills and Quimby Creek runs along the back side of Millbrook Elementary School today. Quimby Road would be one of the third or fourth roads built in Evergreen, after San Felipe Road and Evergreen Road. In fact, Quimby once ran Tully Road’s modern course into town after the turn at Eastridge Mall. The Mall’s creation there was formed by Quimby’s 150 year old route.
John and Minerva would have four kids, while maintaining his political life. Minerva Moody would pass away in 1866, while he was Mayor, and John Alonzo Quimby would remarry the following year. Irene Kamp, the new Mrs. Quimby, and John would have another two children who were also raised in Evergreen. After serving the County for a number of years, John Quimby would become sick for a number of years starting in 1886. Following the illness, Quimby retired from public life to his Evergreen farm. It was said that he too raised vineyards in the Evergreen hills and Quimby Creek runs along the back side of Millbrook Elementary School today. Quimby Road would be one of the third or fourth roads built in Evergreen, after San Felipe Road and Evergreen Road. In fact, Quimby once ran Tully Road’s modern course into town after the turn at Eastridge Mall. The Mall’s creation there was formed by Quimby’s 150 year old route.
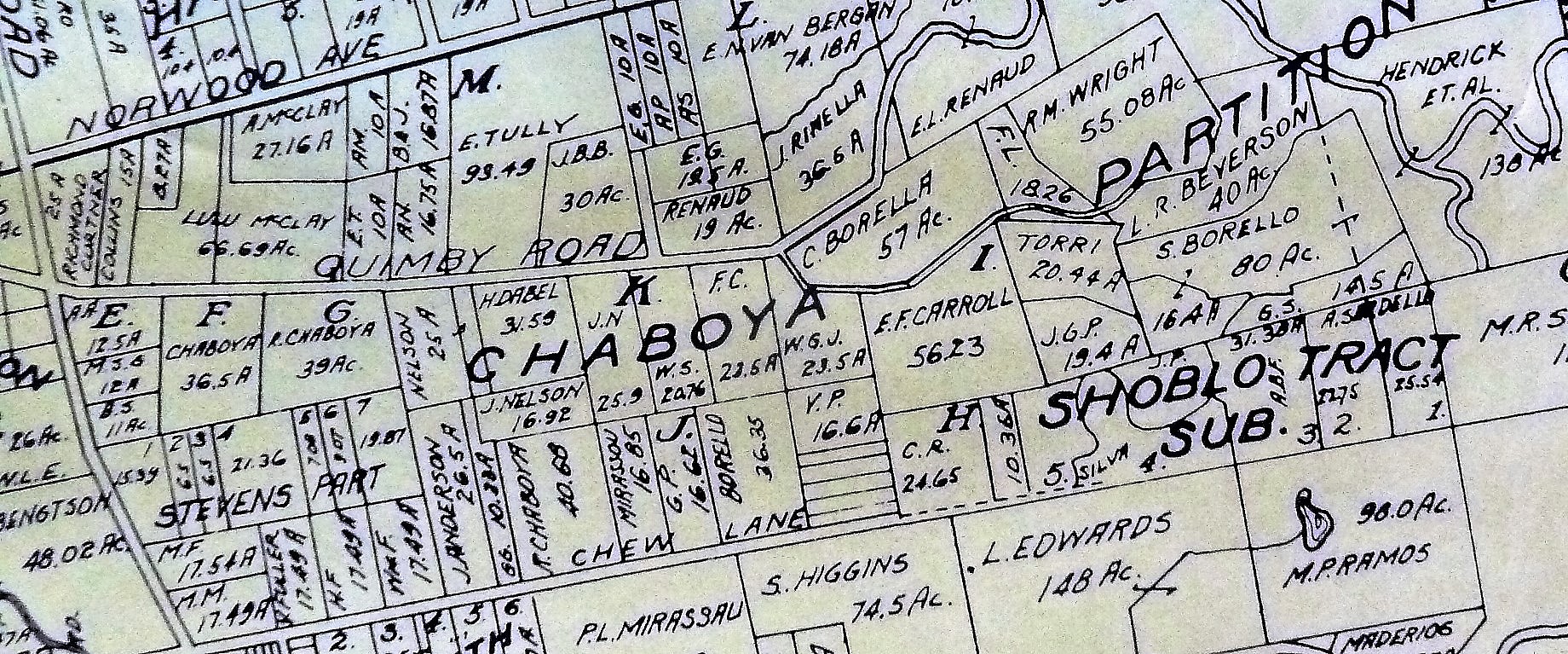 The large Evergreen estate passed to Irene and his family when John Alonzo Quimby passed in 1891. This 1903 map shows a portion of the Quimby Ranch, 55 acres, still held by his daughter, Mrs. R. M. Wright. One of his sons, Fred Alonzo Quimby, carried on the tradition of civic service into the 20th century, though sadly not in Santa Clara County.
The large Evergreen estate passed to Irene and his family when John Alonzo Quimby passed in 1891. This 1903 map shows a portion of the Quimby Ranch, 55 acres, still held by his daughter, Mrs. R. M. Wright. One of his sons, Fred Alonzo Quimby, carried on the tradition of civic service into the 20th century, though sadly not in Santa Clara County.

 Oh, and the awesome Harriet Quimby, first woman to have a pilot’s license, wouldn’t be from Evergreen or San Jose. Instead, she probably heard about the road’s name on a flight to San Jose then lie ruthlessly about it, creating fairytales and misinformation about her early life. Harriet was born in Michigan. She was quite a character, but none of John Alonzo’s sons would marry a woman having a daughter Harriet. She also freely lied about her age. Don’t worry. The Quimby’s are a huge family. She probably wasn’t lying about the name, but could so easily weave misinformation into interviews because of the name’s popularity around the United States.
Oh, and the awesome Harriet Quimby, first woman to have a pilot’s license, wouldn’t be from Evergreen or San Jose. Instead, she probably heard about the road’s name on a flight to San Jose then lie ruthlessly about it, creating fairytales and misinformation about her early life. Harriet was born in Michigan. She was quite a character, but none of John Alonzo’s sons would marry a woman having a daughter Harriet. She also freely lied about her age. Don’t worry. The Quimby’s are a huge family. She probably wasn’t lying about the name, but could so easily weave misinformation into interviews because of the name’s popularity around the United States.
I think the obituaries for John A. Quimby about the most eloquent summarizations and indications of how he was received by his contemporaries, Democrat or Republican. His was admired for both his political achievements and undertakings, as well as for his kindness and hospitality.
“Death of a Pioneer of San Jose – A Public Spirited Citizen – One who has served faithfully in various Public Offices and did much as a Private Citizen” said one local newspaper. Another states “His life here since pioneer days was an active one until a few years ago… made him prominent amount residents of the county.” It goes on, “The pioneer residents of this county will bear willing testimony to the deep regard entertained for the departed [Quimby] by all who had the pleasure and profit of an intimate acquaintance…”
 The Artwork which features J. A. Quimby also features possible inspiration Charles White. After writing this, I’m wondering if we’ve given John Alonzo enough credit either. His leadership created the City we enjoy today, which modern people from Evergreen continue to develop it and serve the same offices. The Simpson’s bumbling Mayor couldn’t be further away from our Mayor Quimby.
The Artwork which features J. A. Quimby also features possible inspiration Charles White. After writing this, I’m wondering if we’ve given John Alonzo enough credit either. His leadership created the City we enjoy today, which modern people from Evergreen continue to develop it and serve the same offices. The Simpson’s bumbling Mayor couldn’t be further away from our Mayor Quimby.
After doing this article, here’s the updated White and Quimby Piece.